
Windows Authentication is the default authentication mode, and is much more secure than SQL Server Authentication. SQL Server does not ask for the password, and does not perform the identity validation. This means that the user identity is confirmed by Windows. When a user connects through a Windows user account, SQL Server validates the account name and password using the Windows principal token in the operating system.
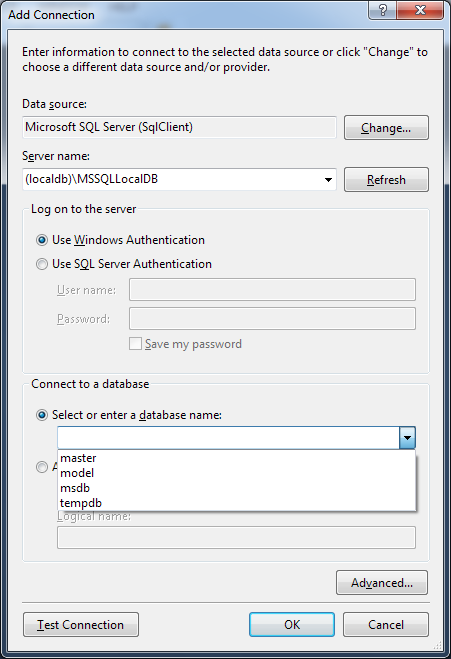
Connecting Through Windows Authentication To change from Windows Authentication mode to Mixed Mode Authentication and use SQL Server Authentication, see Change Server Authentication Mode. Never set a blank or weak password for the sa account. Because the sa account is well known and often targeted by malicious users, do not enable the sa account unless your application requires it. Any Windows or SQL Server account can be configured as a system administrator. If you later change to Mixed Mode Authentication and you want to use the sa account, you must enable the account. If you select Windows Authentication during setup, Setup creates the sa account for SQL Server Authentication but it is disabled. The sa account connects by using SQL Server Authentication. If you select Mixed Mode Authentication during setup, you must provide and then confirm a strong password for the built-in SQL Server system administrator account named sa. Windows Authentication is always available and cannot be disabled. Mixed mode enables both Windows Authentication and SQL Server Authentication. Windows Authentication mode enables Windows Authentication and disables SQL Server Authentication. There are two possible modes: Windows Authentication mode and mixed mode. During setup, you must select an authentication mode for the Database Engine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
